omega 3 fatty acids definition The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.
FAT LV Electrical Boards - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides a checklist for visual inspection of low voltage electrical boards. It lists specifications and requirements for items like switchboard frames, panels, doors, busbars, conductors, and other components.
0 · why omega 3 is important
1 · where is omega 3 found
2 · omega 3 other name
3 · omega 3 food chart
4 · omega 3 fatty acids names
5 · omega 3 fatty acids examples
6 · omega 3 fatty acid facts
7 · nih omega 3 fact sheet
Fci Lv Llc pays an average salary of $4,838,233 and salaries range from a low of $4,256,394 to a high of $5,482,761. Individual salaries will, of course, vary depending on the job, department, location, as well as the individual skills and education of each employee.LV Photo, Las Vegas, Nevada. 5,548 likes. LV Photo is the premier event photography company in Las Vegas for all corporate and special events.
rolex 93250
why omega 3 is important
Omega-3 fatty acids are “healthy fats” that may support your heart health. One key benefit is helping to lower your triglycerides. Specific types of omega-3s include DHA and EPA (found in seafood) and ALA (found in plants). Consuming the right ratio of omega-3, -6 and -9 fatty acids is important for your health. This article explains what these fats are and how to .Omega-3 fatty acids (omega-3s) have a carbon–carbon double bond located three carbons from the methyl end of the chain. Omega-3s, sometimes referred to as n-3s, are present in .
where is omega 3 found
There is strong evidence that omega-3 fatty acids protect a person against atherosclerosis and therefore against heart disease and stroke, as well as abnormal heart rhythms that cause sudden cardiac death, and possibly autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.In fact, Drs. Dean Ornish and Mehmet Oz, renowned heart physicians, said in a 2002 article published .
The balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is unique to hemp seeds. Mackerel: A 3-ounce portion of the fatty fish mackerel provides 0.8 g EPA and 1.2 g DHA. Cod liver oil: A concentrated source of omega-3 .The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.
Omega 3 fatty acids can sell foods and supplements, but the alphabet soup of omega 3, omega 6, DHA, EPA, AA, and AL may be hard to untangle. Here are definitions, information about effects, and recommendations for intake. Why Are Fatty Acids Called "Omega Fatty Acids"? Omega fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats. Omega-3 fatty acids, a name often heard in health discussions, are essential nutrients that pack numerous benefits for the body and mind. When incorporated into daily diets, these fatty acids can redefine well-being, promoting optimal health.
Essential fatty acids include linoleic acid (LA), an omega-6 fatty acid, and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid. These fatty acids make hormones that regulate the immune system and .The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Introduction. Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are essential for the human body. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Omega-3 fatty acids are not produced naturally by the body, so they must be obtained through the diet or supplements.The meaning of OMEGA-3 is being or composed of polyunsaturated fatty acids that have the final double bond in the hydrocarbon chain between the third and fourth carbon atoms from the end of the molecule opposite that of the carboxyl group and that are found especially in fish, fish oils, green leafy vegetables, and some nuts and vegetable oils.
Omega−3 fatty acids, also known as Omega-3 oils, omega - 3 fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids. Omega 3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the .This is a general overview. For more in-depth information, see our health professional fact sheet.. What are omega-3 fatty acids and what do they do? Omega-3 fatty acids are found in foods, such as fish and flaxseed, and in dietary supplements, such as fish oil.. The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and .日本語. Summary. Linoleic acid (LA), an omega-6 fatty acid, and α-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid, are considered essential fatty acids because they cannot be synthesized by humans. (More information) The long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), can be synthesized from ALA, but due to low conversion . Research shows that the three types of omega-3 fatty acids, EPA, DHA, and ALA, may be beneficial for heart health, brain function, joint health, and skin health. EPA and DHA are found in fatty fish and a few other animal foods, while ALA is found in plant foods.
Mackerel is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids; however, one variety known as king mackerel is also high in mercury and the FDA advises individuals who are pregnant or nursing and young children to avoid this type of fish. Atlantic mackerel and Pacific chub mackerel are lower-mercury alternatives.Omega-3 fatty acids are found in foods, such as fish and flaxseed, and in dietary supplements, such as fish oil. The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils C60H92O6 is the molecular formula of omega-3 fatty acids, and the molecular weight is 909.39 g/mol. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are long-chain, whereas Omega-3 fatty acids present in plants are shorter chains. . This document from the Pennington Biomedical Research Center provides information on omega-3 fatty acids. It defines omega-3 fatty acids and describes their main types: ALA, EPA, and DHA. Sources of each type are .
The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.
The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.Read medical definition of Omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids: A class of essential fatty acids found in fish oils, especially from salmon and other cold-water fish, that acts to lower the levels of cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) in the blood. (LDL cholesterol is the "bad" cholesterol.) EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are the two .
Omega-3 fatty acids are used together with lifestyle changes (diet, weight-loss, exercise) to reduce the amount of triglycerides (a fat-like substance) in the blood in people with very high triglycerides. Omega-3 fatty acids are in a class of medications called antilipemic or lipid-regulating agents. Omega-3 fatty acids may work by decreasing . Omega-3 fats play a vital role in our overall health. There are two primary omega-3 fatty acids; eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These occur naturally in animal foods. Additionally, another omega-3 fatty acid – alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) can be found in various plant foods.Thus, because they must be taken in through the diet, they are called essential fatty acids. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids derived from linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, respectively, are needed conditionally by many mammals—they are formed in the body from their parent fatty acids but not always at levels needed to maintain optimal . Like other non-animal sources of omega-3 fatty acids, avocados contain the omega-3 fatty acid ALA, which your body does not use as effectively as EPA and DHA. These more beneficial types only come .
PUFAs are divided into two families, omega-3 (ω-3) and omega-6 (ω-6). ω-3 fatty acids (FAs) have in common a terminal carbon-carbon double bond in the omega three-position, the third bond from the methyl end of the acid, whereas, ω-6 acids have it in the omega six-position, the sixth bond from the methyl end of the fatty acid, respectively.Proposed mechanisms of action of prescription formulations of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. ApoCIII apolipoprotein CIII, Acetyl Co-A acetyl coenzyme A, DGAT diglyceride acyltransferase; FA fatty acid, LPL lipoprotein lipase, TG triglyceride, VLDL very-low-density lipoprotein. The primary components of OM3FA prescription formulations, EPA and DHA, have both been .
omega 3 other name
The two major classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Like all fatty acids, PUFAs consist of long chains of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at one end of the chain and a methyl group at the other.
omega 3 food chart
how often should you replace walking shoes
chanel paris biarritz fragrance

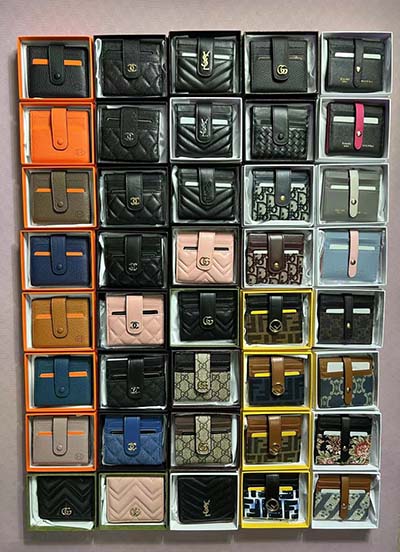
The Favorite is a fashionable bag made from supple grained leather with an oversized embossed Monogram pattern. Feminine pleats bring a couture touch while the gold-color magnetic lock evokes Louis Vuitton’s heritage.
omega 3 fatty acids definition|why omega 3 is important